Principios básicos del diseño del moldeo por inyección
El proceso de moldeo por inyección
El proceso comienza con la fusión de gránulos termoplásticos, la inyección del material fundido en una cavidad de molde diseñada con precisión a alta presión y su enfriamiento para darle la forma deseada. Las etapas clave incluyen:
- Sujeción: Fijación de las mitades del molde.
- Inyección: Rellenar la cavidad con polímero fundido.
- Refrigeración: Solidificación para garantizar la estabilidad dimensional.
- Expulsión: Retirada de la pieza acabada.
La eficacia depende de la optimización del tiempo de ciclo, la selección de materiales y el diseño del molde.
Diseño para la fabricación (DFM)
Los principios de DFM garantizan que los diseños estén optimizados para la producción:
- Espesor de pared uniforme: Evita defectos como marcas de hundimiento y alabeos.
- Ángulos de tiro: Facilitan la expulsión de la pieza (normalmente 1-3°).
- Costillas y refuerzos: Mejore la integridad estructural sin añadir volumen.
- Colocación de la puerta: Controla el flujo de material y minimiza las líneas de soldadura.
- Evitación de socavones: Reduce la complejidad y el coste del molde.
El avanzado software CAD permite realizar simulaciones virtuales para predecir los patrones de llenado, las trampas de aire y las ineficiencias de refrigeración, reduciendo las iteraciones de prototipado.
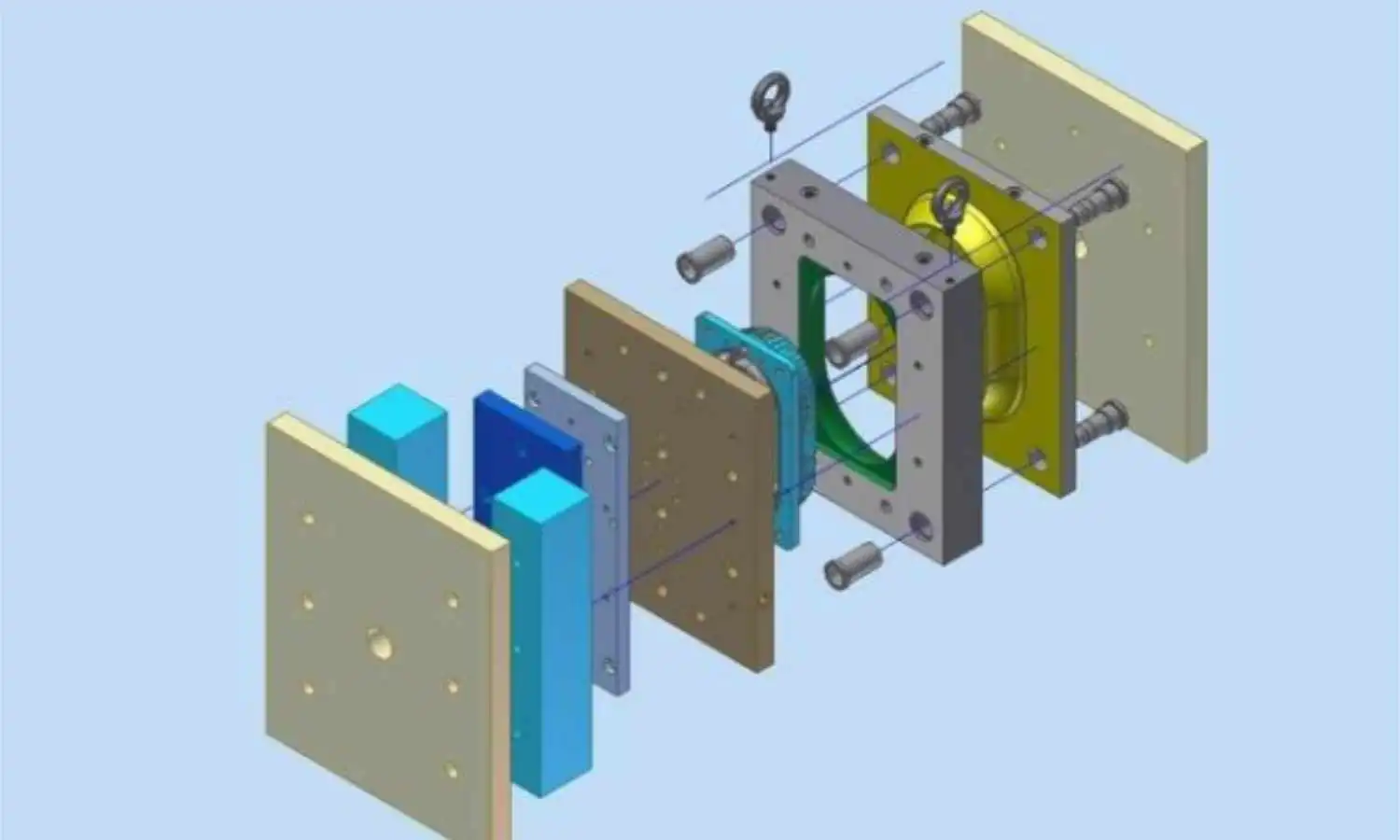
Diseño de moldes: Ingeniería de precisión
Componentes y funcionalidad del molde
Un molde consta de dos mitades (núcleo y cavidad), canales de refrigeración, pasadores eyectores y un sistema de compuerta. Las consideraciones críticas de diseño incluyen:
- Disposición del canal de refrigeración: Garantiza una disipación uniforme del calor para minimizar el tiempo de ciclo.
- Ventilación: Evita el atrapamiento de aire, que causa marcas de quemaduras.
- Acabado superficial: Impacta en la estética de la pieza (por ejemplo, pulido para el brillo, texturizado para el agarre).
Tecnologías avanzadas de moldes
- Refrigeración conforme: Moldes impresos en 3D con canales de refrigeración curvados para un enfriamiento más rápido y uniforme.
- Moldes multicavidad: Permite la producción simultánea de varias piezas.
- Sistemas de canal caliente: Reduzca el desperdicio de material manteniendo el polímero fundido en los canales.
Selección de materiales: Equilibrio entre rendimiento y coste
Los termoplásticos dominan el moldeo por inyección debido a su reciclabilidad y versatilidad. Entre los materiales clave se incluyen:
| Material | Propiedades | Aplicaciones |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | Resistencia a los impactos, durabilidad | Paneles para automóviles, juguetes |
| Policarbonato (PC) | Claridad óptica, resistencia al calor | Gafas de seguridad, productos sanitarios |
| Polipropileno (PP) | Resistencia química, peso ligero | Envases, piezas de automóvil |
| Nylon (PA) | Alta resistencia, resistencia al desgaste | Engranajes, rodamientos |
| PEEK | Estabilidad a altas temperaturas | Aeroespacial, implantes médicos |
Tendencias emergentes:
- Polímeros de base biológica: Reducir la huella de carbono (por ejemplo, PLA).
- Compuestos de fibra de vidrio/carbono: Mejora las propiedades mecánicas.
Optimización de procesos: Control de variables
Los parámetros críticos del proceso incluyen:
- Temperatura de fusión: Afecta a la viscosidad y al flujo.
- Presión/velocidad de inyección: Determina la consistencia del llenado.
- Tiempo de enfriamiento: Impacta en el tiempo de ciclo y en el alabeo de la pieza.
- Mantener la presión: Compensa la contracción durante la solidificación.
Integración de la Industria 4.0:
- Sensores IoT: Supervise los parámetros en tiempo real (presión, temperatura).
- Análisis predictivo: Anticiparse a las necesidades de mantenimiento de las máquinas.
- Gemelos digitales: Simule escenarios de producción para optimizar los ajustes.
Garantía de calidad y sostenibilidad
Métodos de control de calidad
- Inspección dimensional: Las máquinas de medición por coordenadas (MMC) verifican las tolerancias (±0,005-0,1 mm).
- Pruebas mecánicas: Resistencia a la tracción, resistencia al impacto.
- Control estadístico de procesos (CEP): Realiza un seguimiento de las desviaciones en tiempo real.
Prácticas sostenibles
- Reciclaje de materiales: Regrind sprues and runners for reuse.
- Máquinas de bajo consumo: Las prensas totalmente eléctricas reducen el consumo de energía en un 50-70%.
- Aligeramiento: Minimiza el uso de material sin comprometer la resistencia.
Aplicaciones e innovaciones en la industria
- Automoción: Geometrías complejas (por ejemplo, colectores de admisión) con polímeros resistentes al calor.
- Médico: Componentes esterilizables y biocompatibles (por ejemplo, los cuerpos de las jeringuillas).
- Electrónica: Carcasas con blindaje EMI y conectores de precisión.
- Bienes de consumo: Diseños ergonómicos con acabados estéticos.
Tendencias futuras:
- Moldeo multimaterial: Combina polímeros rígidos/flexibles en un solo ciclo.
- Diseño impulsado por la IA: Los algoritmos generativos optimizan la geometría de las piezas en función del peso y la resistencia.
- Economía circular: Sistemas de circuito cerrado para la producción de cero residuos.
Conclusión: El camino hacia la maestría
Dominar el diseño del moldeo por inyección requiere un enfoque multidisciplinar:
- Colaboración: Ingenieros, científicos de materiales y diseñadores deben alinearse en objetivos funcionales y estéticos.
- Aprendizaje continuo: Manténgase al día de los avances en materiales, herramientas de simulación y automatización.
- Enfoque de sostenibilidad: Dé prioridad a los materiales ecológicos y a los procesos eficientes desde el punto de vista energético.
Al integrar la ingeniería de precisión con las tecnologías más avanzadas, los fabricantes pueden lograr una producción rentable y de alta calidad, al tiempo que satisfacen las demandas cambiantes de las industrias globales. El moldeo por inyección sigue siendo no sólo un método de fabricación, sino un catalizador de la innovación en la era digital.