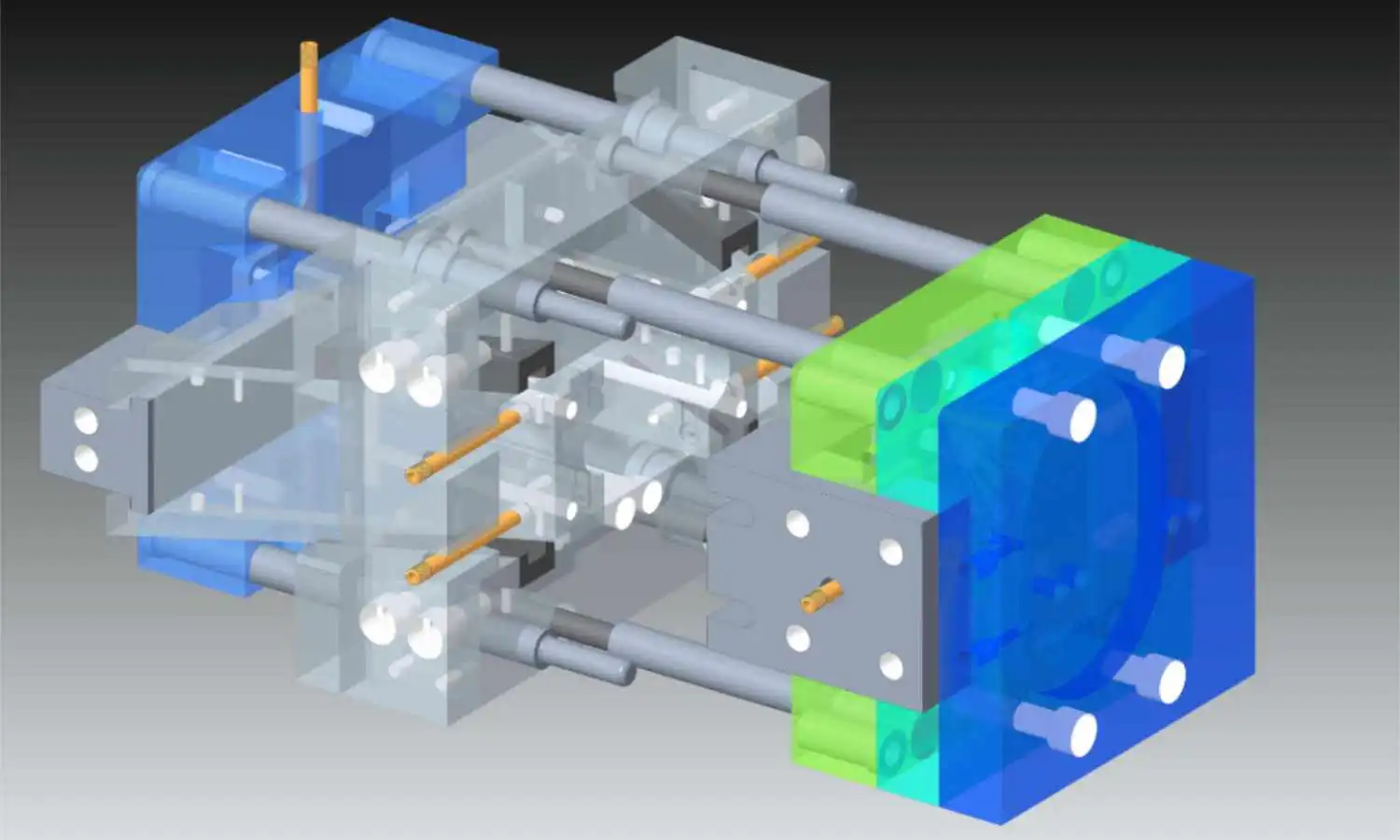
La progettazione degli stampi è la spina dorsale della produzione moderna, che consente la produzione di massa di componenti di precisione in settori come quello automobilistico, medico e dei beni di consumo. Uno stampo ben progettato assicura la coerenza del prodotto, riduce gli scarti e ottimizza l'efficienza produttiva. Questa guida sintetizza i principi critici, le sfide e le tendenze emergenti per consentire ai progettisti di stampi di padroneggiare questa intricata disciplina.
Principi fondamentali della progettazione di stampi
Spessore uniforme della parete
Mantenere uno spessore costante della parete è fondamentale per evitare difetti come segni di affossamento, deformazioni e raffreddamento non uniforme. Le sezioni spesse si raffreddano più lentamente, causando squilibri di contrazione, mentre le pareti sottili rischiano un riempimento incompleto. Per esempio:
- ABS: Lo spessore ottimale della parete varia da 1,14 a 3,56 mm.
- Policarbonato: 1,02-3,81 mm.
Le transizioni graduali (utilizzando filetti o smussi) tra spessori diversi riducono al minimo le concentrazioni di stress.
Angoli di bozza
Gli angoli di sformo facilitano l'espulsione dei pezzi e riducono l'usura degli utensili. Le raccomandazioni variano a seconda del materiale e della finitura superficiale:
- Superfici lisce: 1-2° di bozza.
- Superfici strutturate: Fino a 5° o più.
Le parti fortemente strutturate (ad esempio, gli standard SPI/VDI) richiedono una bozza aggiuntiva per evitare che si attacchino.
Raggi e filetti
Gli angoli acuti ostacolano il flusso del materiale e creano punti di stress. Le linee guida per il design includono:
- Raggi interni ≥50% dello spessore della parete.
- Raggio esterno = raggio interno + spessore della parete.
I bordi arrotondati migliorano l'integrità strutturale e riducono i costi di lavorazione.
Componenti critici dello stampo e strategie di progettazione
Cavità e nucleo
- Cavità: Definisce la forma esterna della parte.
- Nucleo: Forma le caratteristiche interne.
Entrambi devono resistere all'alta pressione e al calore. Gli acciai per utensili (ad esempio, SKD11, SKD61) sono preferiti per la durata, mentre l'alluminio è adatto alla prototipazione. I tassi di espansione termica e di contrazione del materiale devono essere allineati alle proprietà della resina (ad esempio, il PPS richiede una tolleranza di ±0,5%).
Progettazione del sistema di raffreddamento
Un raffreddamento efficace riduce al minimo il tempo di ciclo e i difetti:
- Raffreddamento conformazionale: I canali stampati in 3D seguono i contorni delle parti per una dissipazione uniforme del calore.
- Posizionamento del canale: Posizionare vicino a sezioni spesse per evitare che si deformino. I refrigeranti ad acqua o ad olio sono comuni.
Un cattivo raffreddamento è responsabile di 70% del tempo di ciclo; i sistemi ottimizzati possono ridurlo di 30%.
Sistema di espulsione
- Perni di espulsione: Posizionare su superfici piane per evitare segni. Per le geometrie complesse, utilizzi delle piastre spelacavi.
- Bozza di allineamento: Si assicuri che i perni siano allineati con la direzione di estrazione dello stampo per evitare danni.
I materiali morbidi (ad esempio, il TPE) possono richiedere perni più larghi per distribuire la forza.
Cancelli e corridori
- Tipi di cancelli: Cancelli a bordo (convenienti), cancelli a punta calda (parti estetiche) e cancelli a tunnel (auto-trimming).
- Design del corridore: Bilancia il flusso negli stampi a più cavità. I canali caldi riducono gli scarti nella produzione di grandi volumi.
Il posizionamento del cancello in sezioni spesse assicura un riempimento adeguato e riduce al minimo il getto.
Selezione del materiale per gli stampi
| Materiale | Punti di forza | Applicazioni |
|---|---|---|
| Acciaio temprato (SKD61) | Alta resistenza all'usura, durata | Produzione ad alto volume |
| Alluminio | Leggero, conveniente | Prototipi, volumi ridotti |
| Rame berillio | Conducibilità termica superiore | Stampi che richiedono un raffreddamento rapido |
| Acciaio pre-indurito | Costo e durata equilibrati | Cicli di produzione moderati |
Flusso di lavoro della progettazione per gli ingegneri degli stampi
- Analisi del prodotto: Valutare la producibilità, identificare i sottosquadri, le pareti sottili e i requisiti di tolleranza.
- Selezione del materiale: Abbinare le proprietà della resina (ad esempio, contrazione, stabilità termica) al materiale dello stampo.
- Layout di raffreddamento: Utilizza le simulazioni CAE per ottimizzare il posizionamento dei canali.
- Layout dello stampo: Decidere il numero di cavità (singola o multi-cavità) e il posizionamento del gate.
- Simulazione e test: Convalidare il flusso, il raffreddamento e l'espulsione tramite un software (ad esempio, Moldflow) prima della prototipazione.
Tendenze future nella progettazione di stampi
- Produzione additiva: Gli stampi stampati in 3D consentono una prototipazione rapida e geometrie complesse (ad esempio, strutture reticolari).
- Design guidato dall'AI: L'apprendimento automatico ottimizza il posizionamento del gate, il raffreddamento e la selezione del materiale.
- Sostenibilità: Le resine biodegradabili e i materiali riciclati riducono l'impatto ambientale.
- Integrazione dell'Industria 4.0: Monitoraggio in tempo reale di pressione, temperatura e flusso tramite sensori incorporati.
Conclusione
I progettisti di stampi sono un ponte tra creatività e ingegneria, trasformando i concetti di prodotto in realtà producibili. Aderendo a principi come lo spessore uniforme delle pareti, il raffreddamento strategico e l'ottimizzazione dei materiali, e abbracciando allo stesso tempo innovazioni come l'AI e la produzione additiva, guidano l'efficienza e la qualità della produzione moderna. Con l'evoluzione delle industrie, il ruolo dei progettisti di stampi rimarrà fondamentale per ottenere una produzione sostenibile e di alta precisione.